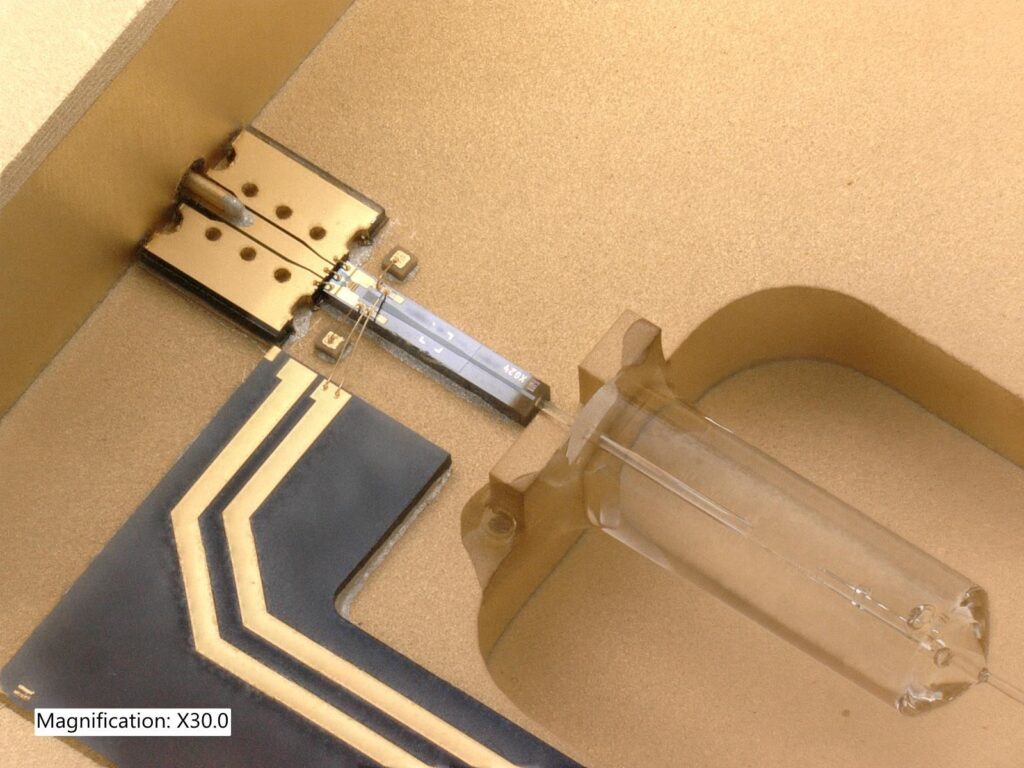
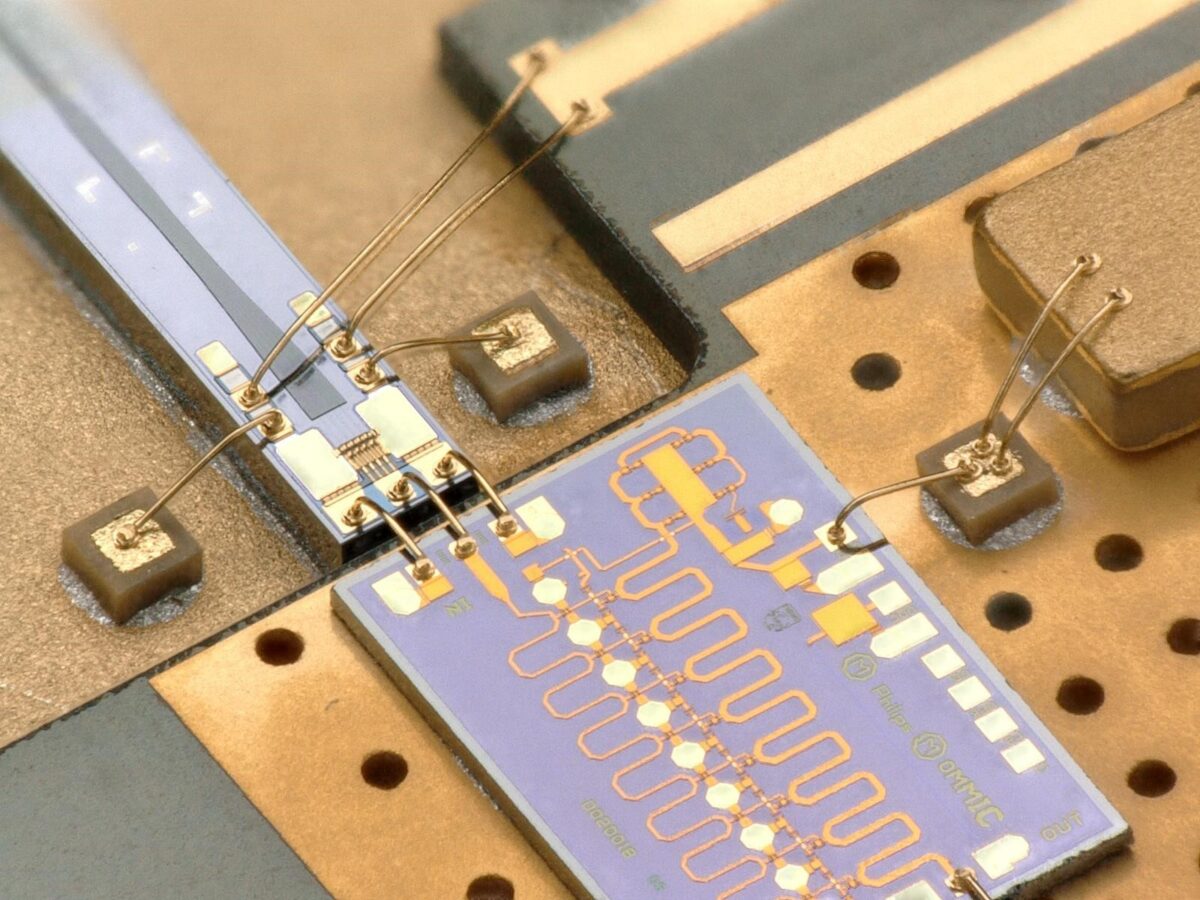
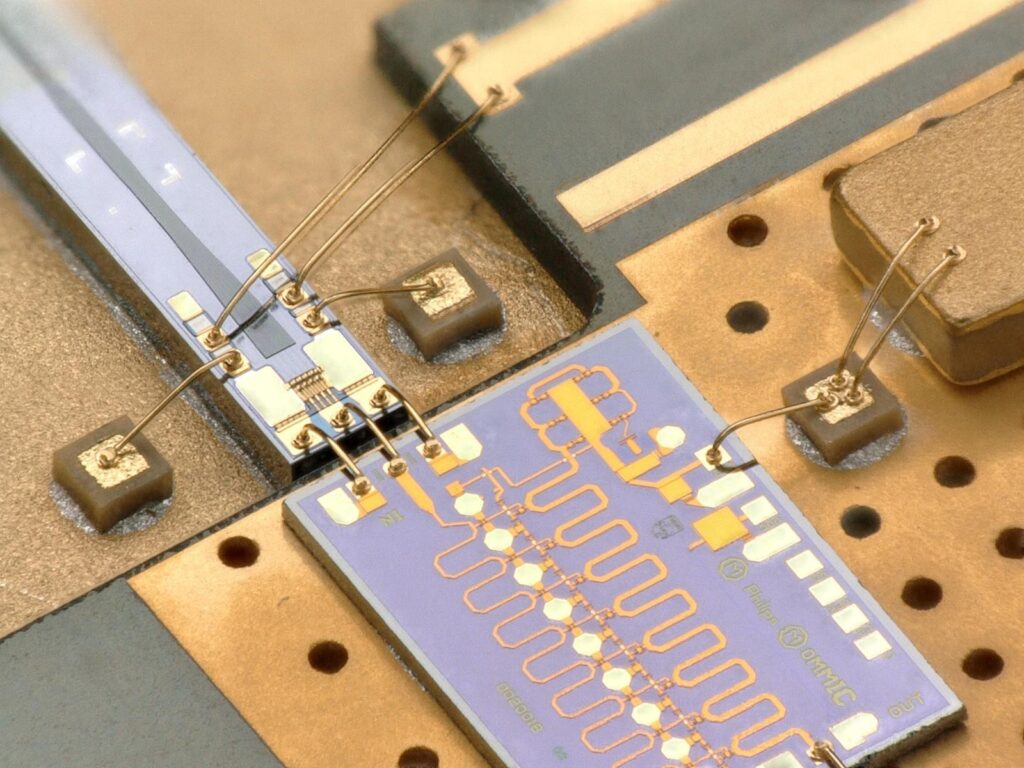
Czech startup Dartsat, which develops ground stations for satellite communications, is preparing a technology collaboration with the European Digital Innovation Hub (EDIH) Brain 4 Industry (B4I).

The B4I hub focuses on providing support for digital innovation and transformation of manufacturing in key industries. Startup Dartsat consulted ESA Technology Broker on the possibility of rapid prototyping of feedhorn holder of its terrestrial antenna and the B4I hub, with its cutting-edge additive manufacturing technologies, was selected as the best option. As part of the EDIH services, this component will be created using a 3D metal printing method. The startup will thus be significantly closer to the first functional product of its ground station.
The availability of rapid prototyping methods is an important factor for the success of all technology companies, but for startups it can play a key role. In this sense, EDIH’s services are essential and space companies can become important clients alongside traditionally targeted sectors such as automotive, energy, aerospace and others.